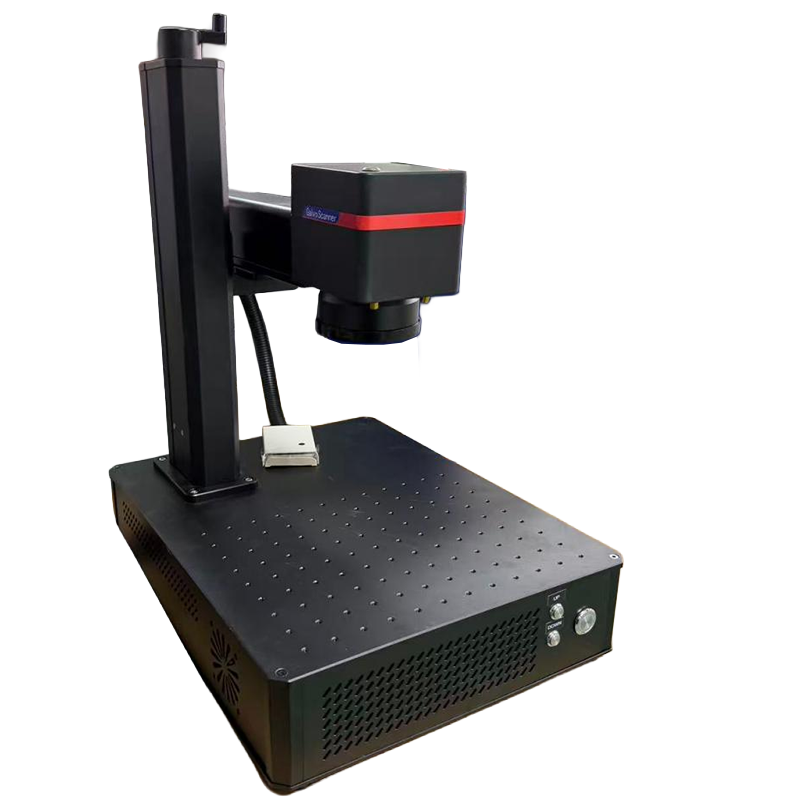
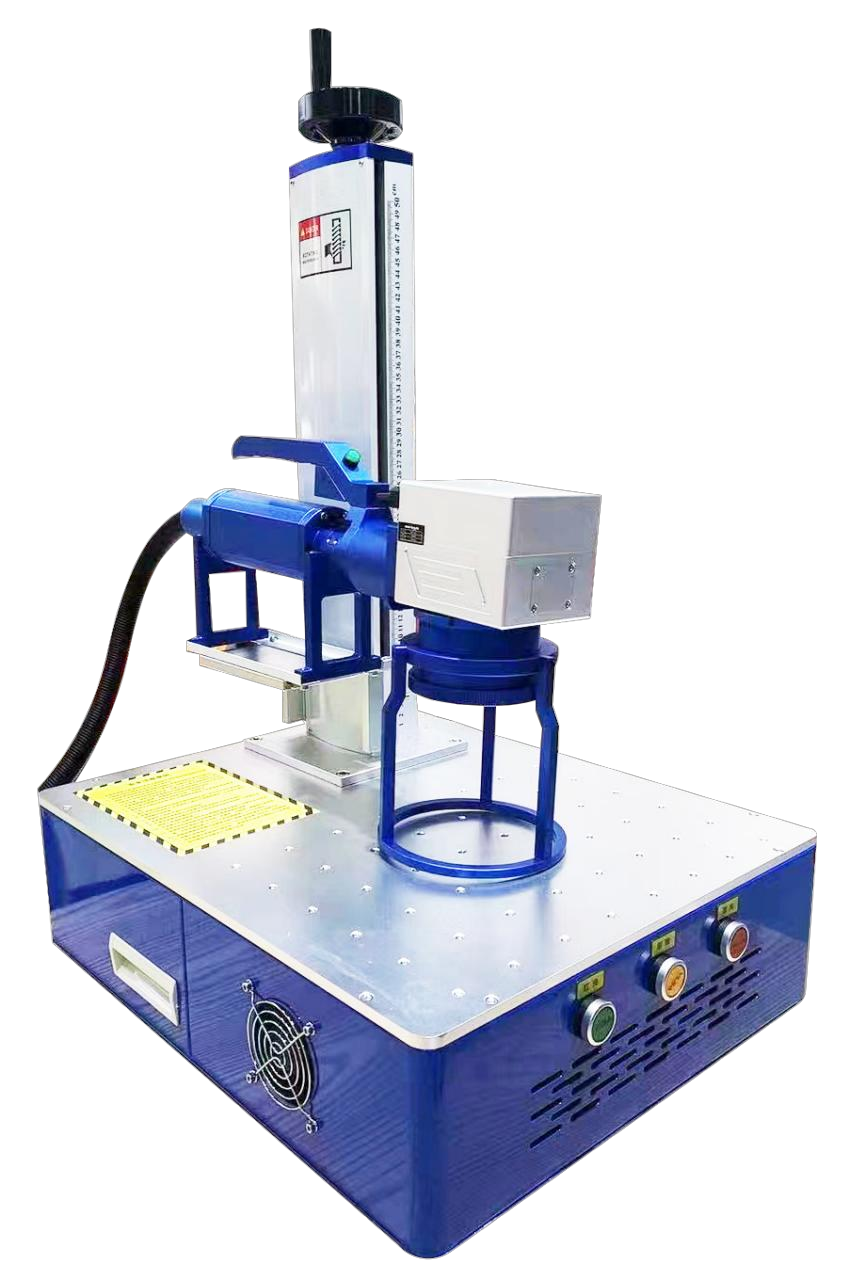
Laser Marking — Making Every Product Unique
In the era of intelligent manufacturing and full lifecycle management, every product should have a unique 'digital ID.' As a core tool to achieve this vision, laser marking technology is encoding everything in a non-contact, permanent, and high-resolution way, making traceability possible. From nanoscale QR codes on chips to high-temperature markings on aircraft engines, laser marking technology not only 'engraves' product identities but also builds the underlying foundation for industrial digitization.
01 Laser Marking: How to 'Engrave' an Identity for Products
The core principle of laser marking is to use a high-energy laser beam to create physical or chemical changes on the surface of a material, forming a permanent mark. Its operation varies depending on the material properties and marking requirements, and mainly includes:
Ablation marking: A high-energy density laser beam directly vaporizes the surface material, exposing the underlying contrasting color to create clear markings. This is commonly used for deep engraving on materials such as metal, plastic, and ceramics. For example, when marking a logo on a stainless steel knife, the laser beam vaporizes the surface oxide layer, revealing the silver metal base and forming a high-contrast mark.
Color-changing marking: By controlling the laser energy density, an oxidation or carbonization reaction is triggered on the material surface, changing its color without damaging the structure. This technique is particularly suitable for marking QR codes or barcodes on metals such as aluminum and titanium alloys, resulting in attractive and wear-resistant marks.
Foaming/bubbling marking: Tiny bubbles are formed inside materials like plastic or glass, and visible patterns are created through the arrangement of these bubbles. This technology is often used for anti-counterfeiting labels on cosmetic packaging, producing marks with a three-dimensional effect that are difficult to replicate.
Micro-nano marking: Using ultrashort pulse lasers (picosecond or femtosecond lasers), the surface of a material is modified at the nanometer scale to form ultra-high-resolution markings. For example, micron-level circuit patterns can be marked on chip packaging with a precision of up to 0.5 μm.
02 Core Advantages: Durable, Precise, Environmentally Friendly
The advantages of laser marking lie not only in its technical principles but also in the multidimensional value it brings:
Permanently readable: The marks are resistant to high temperatures (up to 1200°C), corrosion (extreme acidic and alkaline conditions), and wear (hardness above HRC60), allowing long-term preservation even in extreme environments. For example, identification on certain petroleum drilling equipment must withstand deep-sea pressure and salt spray corrosion, yet the equipment numbers marked by laser remain clearly legible even after 10 years of service.
High precision and high resolution: The minimum character height can reach 0.15mm, and QR code density can reach 25×25mm, meeting the high standards required in precision electronics, medical devices, and other demanding applications. On the SIM card tray of an iPhone, the serial number characters marked by laser are only 0.3mm, almost invisible to the naked eye but can be quickly recognized through machine vision.
Eco-friendly and consumable-free: No need for ink or solvents, no pollution emissions, compliant with environmental regulations such as EU RoHS and REACH. After a packaging and printing company switched to laser marking, they reduced ink usage by 50 tons annually, saving 2 million yuan in costs.
High-speed integration: Marking speed can reach 12,000 characters per second, and it can run in sync with production lines, achieving high-speed marking of hundreds of items per minute. On beverage filling lines, laser marking machines can perform real-time marking of production dates while bottle caps rotate at high speed, with an error rate of less than 0.01%.
Traceable data: By connecting laser marking to industrial internet platforms, each product's code can be linked to production time, equipment parameters, and quality inspection data, enabling full-process traceability. A milk powder company once traced and recalled problematic batches within 48 hours through laser-marked QR codes, avoiding a brand crisis.
03 Application Scenarios: Comprehensive Penetration from Industry to Everyday Life
Laser marking technology has permeated various aspects of daily life from industrial manufacturing:
Electronics and appliances: marking serial numbers, production dates, and QR codes on PCBs, chips, and phone cases to achieve full lifecycle traceability from raw materials to end products. On Samsung Galaxy phone batteries, laser-marked QR codes can be linked to battery charge-discharge cycles and health status, providing data support for after-sales service.
Pharmaceutical packaging: Mark batch numbers, expiration dates, and drug ingredients on medicine bottles, syringes, and infusion bags to ensure medication safety. A vaccine manufacturer uses laser marking to create invisible QR codes, which, combined with special detection equipment, effectively prevent vaccine counterfeiting.
Automotive parts: Assign unique codes to key components such as engines, transmissions, and brake discs to facilitate after-sales tracking and quality analysis. Each Tesla battery module has a laser-marked "electronic ID card," allowing precise identification of the production team and process parameters.
Luxury goods and anti-counterfeiting: Achieve anti-counterfeiting verification through invisible code and microcode technology to protect brand value. On the metal accessories of LV handbags, laser-marked nanoscale QR codes need to be recognized under a microscope, which greatly increases the difficulty of counterfeiting.
Food packaging: Mark the production date and traceability information on meat and dairy packaging to meet the requirements of food safety regulations. A meat processing enterprise uses laser marking QR codes, and consumers can scan the code to view the whole process information of breeding, slaughtering and transportation.
04 Future prospects: deep integration with the industrial Internet
Laser marking is evolving from a "marking tool" to a "data entry" and has become a key part of intelligent manufacturing:
AI-powered intelligent marking: Through machine vision and AI algorithms, laser marking machines can automatically identify product surface features, dynamically adjust focal length and power, and achieve accurate marking of irregular surfaces. For example, in the curved surface marking of automotive wheels, the AI system can optimize the spot path in real time based on the shape of the wheel.
Blockchain laser marking: Write product codes into the blockchain to ensure that the data cannot be tampered with, creating a credible supply chain system. A diamond company uses a laser to mark the diamond's waist with nanoscale coding and bind it to the blockchain, so that consumers can verify the origin and quality of the diamond at any time.
Metamaterial marking: Fabricate special micro-nano structures on the surface of materials, and give them functionality through laser marking, such as antibacterial, anti-fingerprint, and transparency enhancement. For example, laser marking micro-nano textures on the back panel of the mobile phone glass can improve the anti-fingerprint performance of the screen.
Metaverse and NFT marking: Mark NFT codes for physical products, bind physical products to digital assets, and open up a new business model for the integration of virtual and real. A trendy brand sneaker uses a laser marking NFT QR code, and consumers can get exclusive digital collections after purchase.
Laser marking technology allows every product to have a "digital vocal cord". In the wave of Industry 4.0 and digital economy, it is not only the "engraver" of product identity, but also the "starting key" of data flow. From product traceability, brand protection to virtual and real interaction, laser marking is redefining the relationship between "manufacturing" and "connection", laying a solid logo foundation for the era of the Internet of Everything.




Post time: 12-31-2025